“The Prisoner's Kaleidoscope”
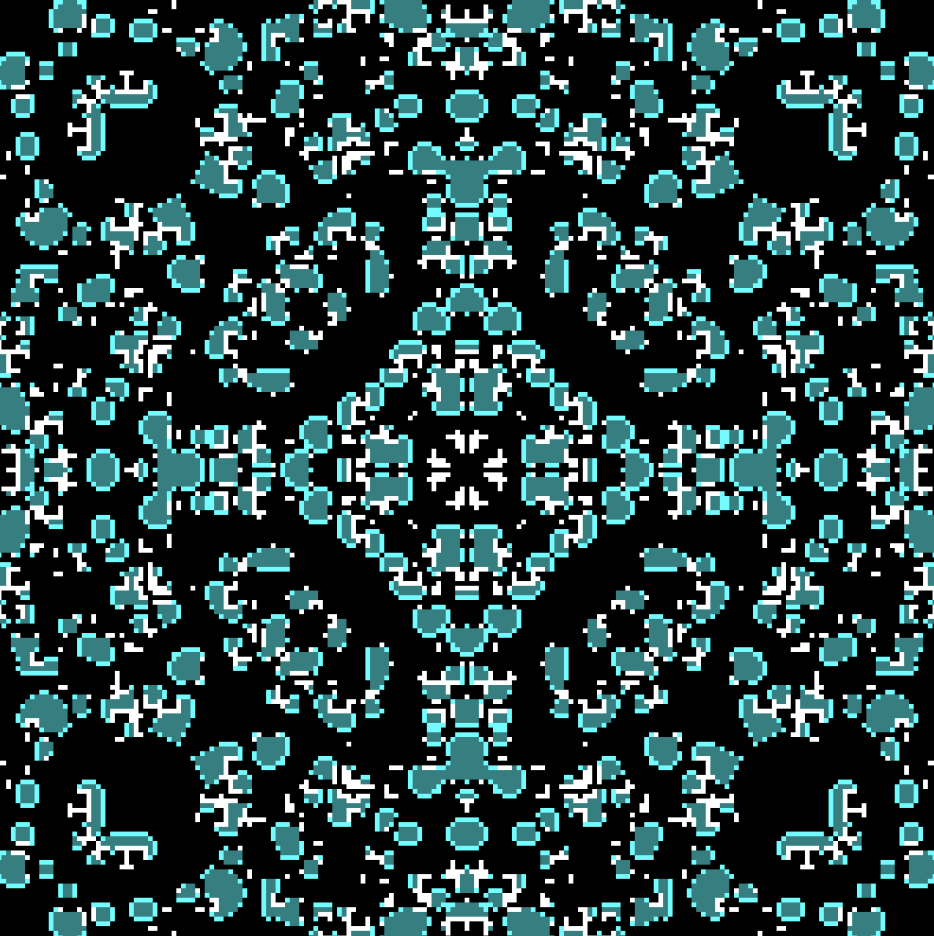
The prisoner's dilemma game on a lattice
This explorable illustrates beautiful dynamical patterns that can be generated by a simple game theoretic model on a lattice. The core of the model is the Prisoner’s Dilemma, a legendary game analyzed in game theory. In the game, two players can choose to cooperate or defect. Depending on their choice, they receive a pre-specified payoffs. The payoffs are chosen such that it seems difficult to make the right strategy choice.
“Horde of the Flies”
The Vicsek-Model
This explorable illustrates one of the most famous and most fundamental models for the emergence of flocking, swarming and synchronized behavior in animal groups. The model was originally published in a 1995 paper by Tamás Vicsek and co-workers and is therefore called the Vicsek-Model. The model can explain why transitions to flocking behavior in groups of animals are often not gradual. Instead, one can expect a sudden emergence of flocking and synchronized movements if a critical density is crossed.
“Eigenartig”
The spatial hypercycle model
This explorable illustrates the dynamics of the famous hypercycle model. It was originally conceived by Peter Schuster and Nobel laureate Manfred Eigen (1927-2019) in 1979 to investigate the chemical basis of the origin of life. Because living things make copies of themselves, in the beginning complex chemicals like polymer chains, including small RNA molecules (see e.g. RNA-world), had to acquire the ability to catalyse their own synthesis from smaller parts, e.g. single nucleotides.
“Come Together”
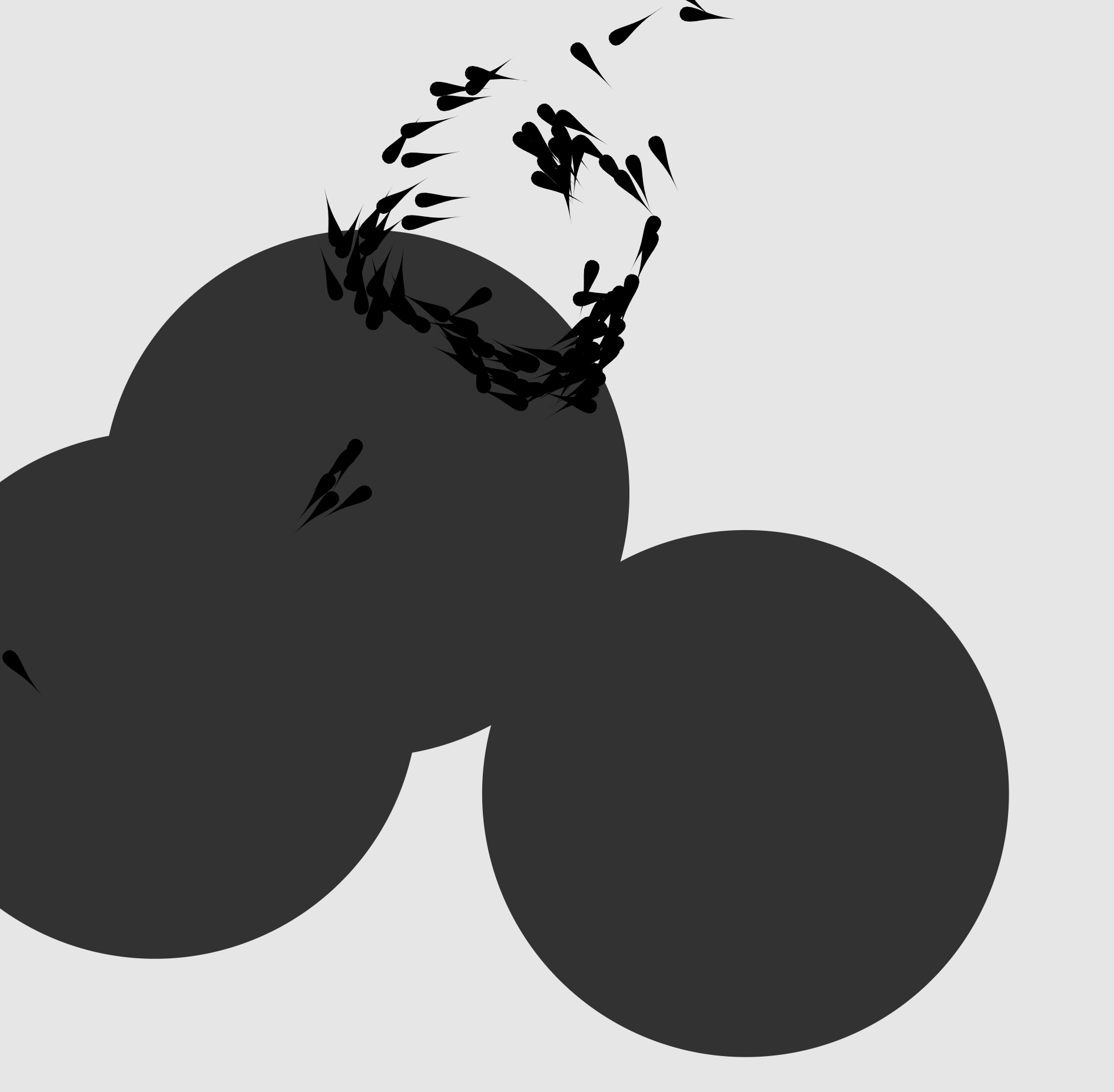
Chemotaxis in Dictyostelium discoideum
This explorable illustrates how simple, single-cell organisms can manage to aggregate into multi-cellular structures by emitting and responding to chemical signals. Individual cells respond by orienting towards a chemical signal and moving up its gradient, a process known as chemotaxis. The combination of synchronized signal emission and chemotaxis yields collective behavior with beautiful spatial branching patterns during the aggregation process.
“Repliselmut”
Yet another Complexity Explorable on evolution
This explorable illustrates how variation and selection in a population of replicating organisms naturally leads to a gradual increase in the population’s overall fitness. The explorable simulates a system that is captured (to some extent) by the Replicator-Mutator Equation which is both, a generalization of the famous Replicator Equation and the Quasispecies Equation.
“Critically Inflammatory”
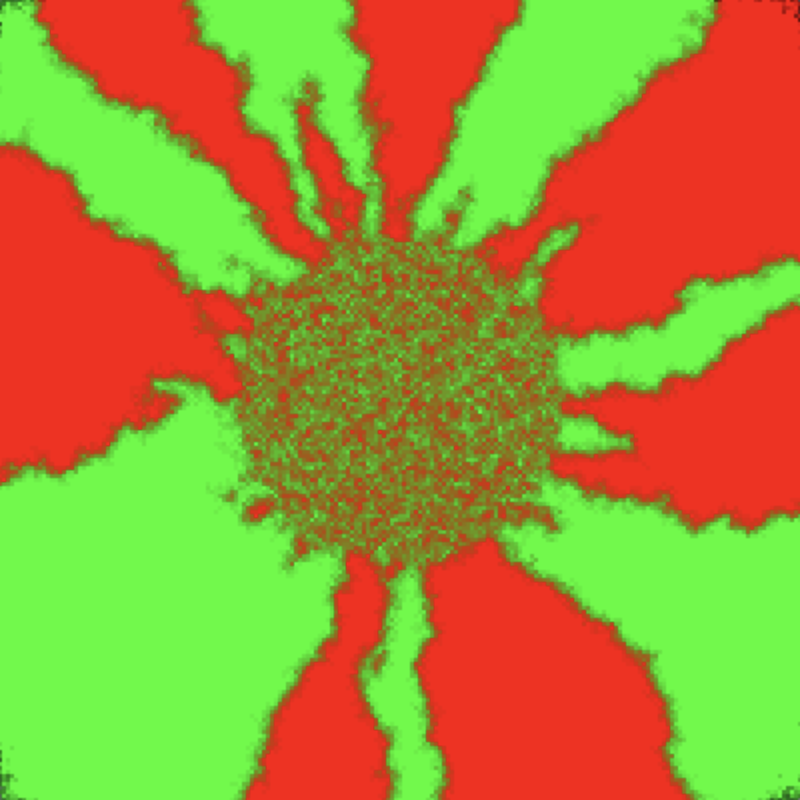
A forrest fire model
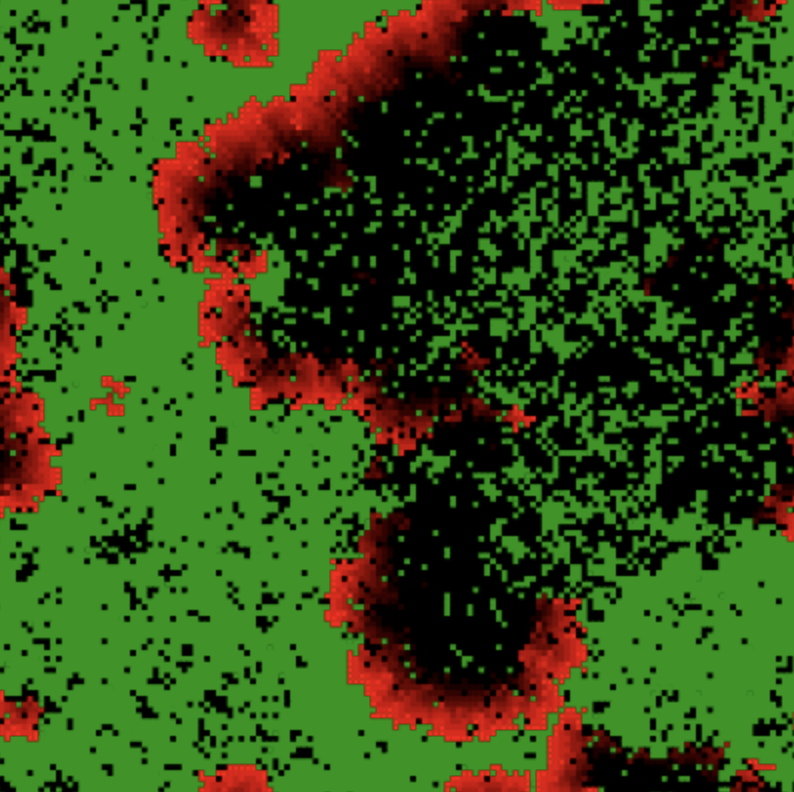
This explorable illustrates, as a representative of a broad range of dynamic phenomena, a simple model for the spatial spread of forest fires and the dynamic patterns they generate. In the model two antagonistic processes interplay, the reproductive growth of vegetation that continuously covers the landscape with trees susceptible to fires and spontaneously seeded (lightning strikes) forest fires that spread across areas of dense vegetation.
“Surfing a Gene Pool”
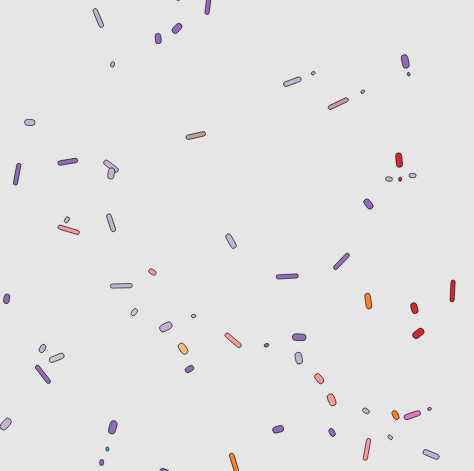
Expansion of clones with idential fitness
This explorable is about pattern formation in a model system for the growth of a bacterial population in a petri dish in which the bacterial population is made up of a mix of two or three mutant strains that have identical fitness and reproduction properties. In the model system, an initially well mixed drop of bacteria with an equal amounts of every mutant strain is positioned in the center of the petri dish. After that, the bacteria start replicating, the population expands radially and a pattern will emerge.
“Maggots in the Wiggle Room”
The dynamics of evolution
This explorable illustrates an evolutionary process in an “ecosystem” of interacting species (cartoon maggots, in this case). Individuals move around in their enviroment, replicate and eat each other. Optionally, mutations can generate new species. The system is similar to the Explorable A Patchwork Darwinge, only a bit more animalistc and dynamically slightly different. However, for this one here, you need a bit more patience in order to observe interesting effects.
“A Patchwork Darwinge”
Evolution: Variation and Selection
This explorable illustrates how the combination of variation and selection in a model biological system can increase the average fitness of a population of mutants of a species over time. Fitness of each mutant quantifies how well it can reproduce compared to other mutants. Variation introduces new mutants. Sometimes a mutant’s fitness is lower than its parent’s, sometimes higher. When lower, the mutant typically goes extinct, if higher the mutant can outperform others and proliferate in the population. This way mutants with higher fitness are naturally selected.
“Into the Dark”
Collective intelligence
This explorable illustrates how a school of fish can collectively find an optimal location, e.g. a dark, unexposed region in their environment simply by light-dependent speed control. The explorable is based on the model discussed in Flock’n Roll, which you may want to explore first.
“Lotka Martini”
The Lotka-Volterra model
This explorable illustrates the dynamics of a predator-prey model on a hexagonal lattice. In the model a prey species reproduces spontaneously but is also food to the predator species. The predator requires the prey for reproduction. The system is an example of an activator-inhibitor system, in which two dynamical entities interact in such a way that the activator (in this case the prey) activates the inhibitor (the predator) that in turn down-regulates the activator in a feedback loop. Activator-inhibitor systems often exhibit oscillatory behavior, like the famous Lotka-Volterra System, a paradigmatic model for predator prey dynamics.
“Critical HexSIRSize”
The stochastic, spatial SIRS model
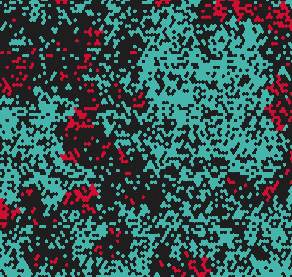
This explorable illustrates the behavior of a contagion process near its critical point. Contagion processes, for example transmissible infectious diseases, typically exhibit a critical point, a threshold below which the disease will die out, and above which the disease is sustained in a population. Interesting dynamical things happen when the system is near its critical point.
“Cycledelic”
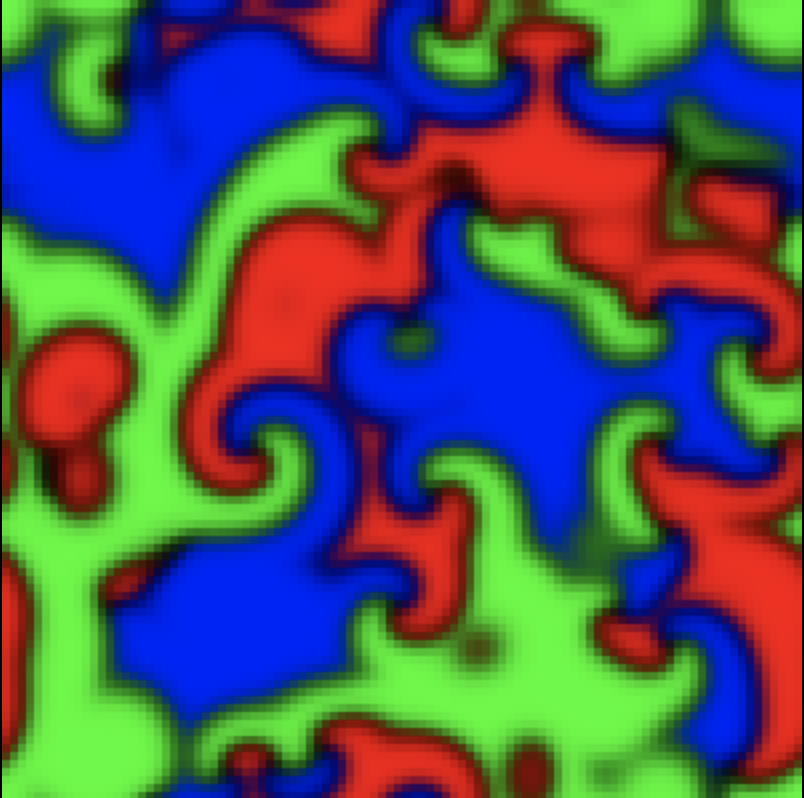
The spatial rock-paper-scissors game
This explorable of a pattern forming system is derived from a model that was designed to understand co-existance of cyclicly interacting species in a spatially extended model ecosystem. Despite its simplicity, it can generate a rich set of complex spatio-temporal patterns depending on the choice of parameters and initial conditions.